Obesity has emerged as a significant public health concern worldwide. Beyond its visible physical effects, excess body weight is associated with several serious medical conditions, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and various cancers. Among these, colorectal cancer has shown a strong and well-established association with overweight and obesity.

Clinical research consistently indicates that individuals with higher body mass index (BMI) have an increased risk of developing colorectal cancer compared to those with a healthy weight. Understanding this relationship is essential for prevention, early detection, and timely treatment.
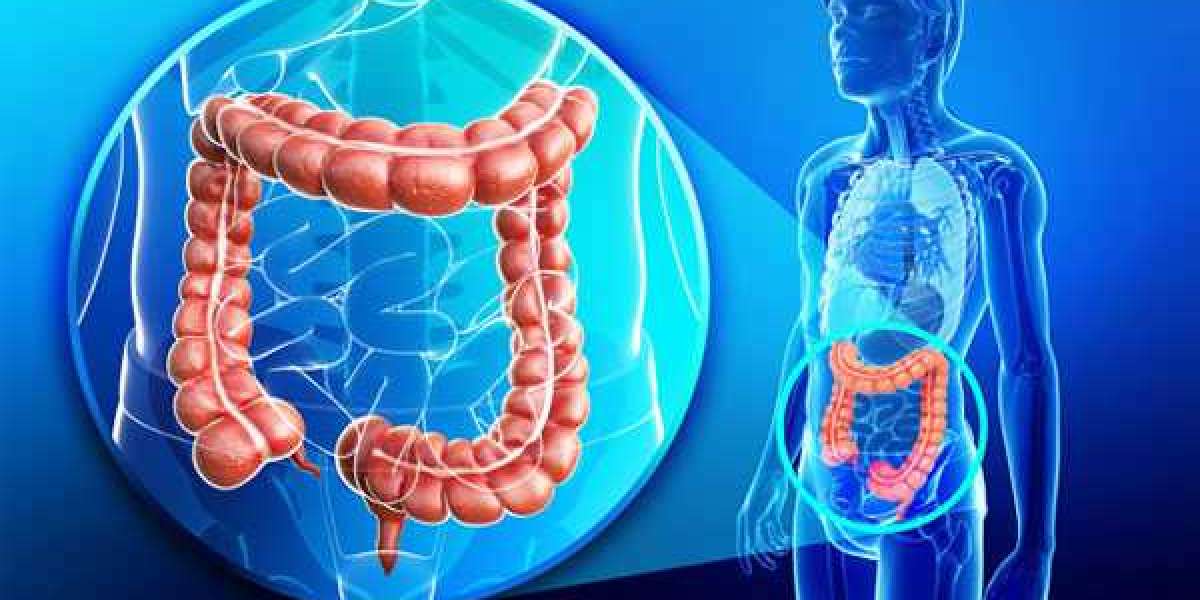
What Is Colorectal Cancer?
Colorectal cancer develops in the colon or rectum, which form the large intestine. It usually begins as small, non-cancerous growths called polyps on the inner lining of the colon. Over time, some polyps may undergo malignant transformation and progress into cancer.
This cancer often develops gradually over several years, making regular screening highly effective in detecting precancerous lesions at an early stage. Common symptoms may include:
- Persistent changes in bowel habits
- Blood in stool
- Abdominal discomfort or cramping
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue or anemia
Age, genetic predisposition, and family history are important risk factors. However, lifestyle-related factors — including diet, physical inactivity, and obesity — play a major role in disease development.
How Does Obesity Increase the Risk?
Excess body fat influences cancer development through several biological mechanisms:
- Hormonal imbalance: Obesity increases insulin and insulin-like growth factors, which can promote abnormal cell growth.
- Chronic inflammation: Fat tissue produces inflammatory substances that may contribute to cancer progression.
- Metabolic dysfunction: Obesity is often associated with diabetes and metabolic syndrome, which further elevate cancer risk.
Additionally, obesity may complicate cancer treatment. It can influence drug dosing, increase surgical risk, and contribute to other medical conditions that affect recovery.
Reducing the Risk of Colorectal Cancer:
Maintaining a healthy weight is one of the most effective ways to reduce colorectal cancer risk. Preventive strategies include:
- Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate physical activity per week
- Incorporating strength training exercises regularly
- Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Limiting red and processed meats
- Avoiding smoking
- Reducing alcohol intake
- Undergoing regular screening, especially after age 45 or earlier if there is a family history
Early detection significantly improves survival outcomes.
Is Surgery Enough to Cure Colorectal Cancer?
Surgery is a cornerstone of treatment for localized colorectal cancer. The goal is to remove the tumor along with nearby lymph nodes to prevent spread. However, depending on the stage of the disease, surgery alone may not be sufficient.
In many cases, chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy are recommended alongside surgery to reduce recurrence risk. Treatment planning is individualized based on tumor stage, location, patient age, and overall health.
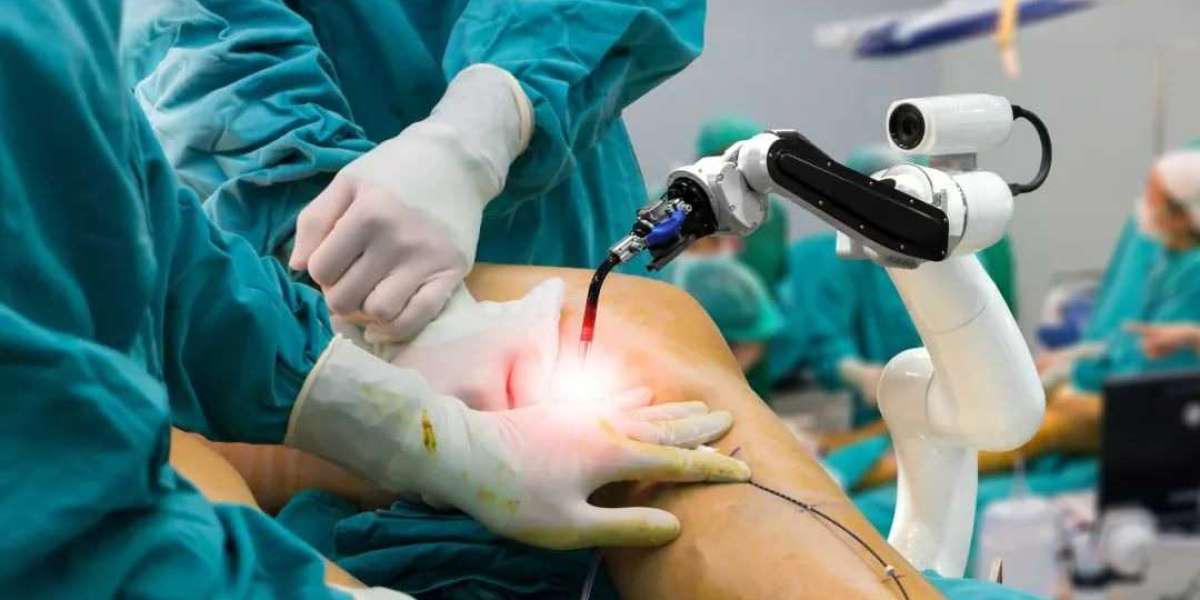
Advanced Colorectal Surgery in Delhi incorporates minimally invasive and robotic techniques, allowing precise tumor removal with quicker recovery and fewer complications when performed by an experienced specialist.
Expert Care Matters:
Choosing a skilled Cancer Surgeon in Delhi is critical for achieving the best outcomes. Dr. Neeraj Goel, a leading GI and colorectal specialist, provides comprehensive evaluation and advanced Colorectal Surgery in Delhi using modern surgical techniques and multidisciplinary cancer care.
With timely screening, healthy lifestyle choices, and expert medical guidance, colorectal cancer can often be prevented or treated effectively. Early consultation remains the key to better prognosis and improved quality of life.